by David Schwalenberg
February 26, 2016
Vulnerabilities in applications and application development can be a great risk to an organization. Vulnerabilities in application development include common coding errors, using vulnerable libraries or components, or having vulnerable development kits on the network. Applications on the network that are vulnerable or unsupported also pose a serious risk. Vulnerabilities within applications could allow attackers to compromise the network and steal or destroy data. Development tools that are accessible in insecure locations could allow an intruder to modify code and functionality for malicious purposes. This dashboard highlights these vulnerabilities in order to assist the organization in securing its application development and lifecycle management.
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) provides guidance based on existing standards, guidelines, and practices, which can be tailored to specific organizational needs. This dashboard aligns with the CSF subcategory PR.IP-2 that deals with secure development and life cycle management. This dashboard includes several components that identify actively and passively detected vulnerabilities in application and web development products by vendor. For example, under Application Development, vulnerabilities in Microsoft products such as .Net and VBScript are noted, and under Web Development, vulnerabilities in Adobe products such as Dreamweaver and GoLive are noted. These detections not only help identify vulnerable development tools, but also indicate where these tools are available on the network. A component highlighting detected vulnerabilities associated with the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Top Ten web application flaws is included on the dashboard, as well as a table of all unsupported products detected on the network.
A component is also included that uses plugin name keywords to highlight detections of common application development errors and vulnerabilities in development kits, libraries, and common IDEs. An organization can develop its own Nessus or NNM plugins to discover vulnerabilities associated with its own internal software development; these detections will automatically appear in this component if the plugin names contain the appropriate keywords. New indicators can also be added as desired.
Analysts can also use this dashboard to easily drill down into the data presented by the dashboard components. This enables the analyst to gain more detailed information about the vulnerabilities found on the network, such as which vulnerabilities are most dangerous or most common. The analyst can also determine information that will benefit vulnerability mitigation. This information might include on which hosts a vulnerability is found and what remediations would most benefit a particular group of machines. Knowing these details can enable better and more efficient patching and mitigation of application development vulnerabilities within the organization, as well as enabling removal of development tools that are in insecure locations.
This dashboard and its components are available in the Tenable.sc Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Tenable.sc Feed under the category Compliance & Configuration Assessment. The dashboard requirements are:
- Tenable.sc 5.2.0
- Nessus 8.5.0
- LCE 6.0.0
- NNM 5.9.0
Tenable.sc Continuous View (Tenable.sc CV) is the market-defining continuous network monitoring platform. Tenable.sc CV includes active vulnerability detection with Nessus and passive vulnerability detection with the Nessus Network Monitor (NNM), as well as log correlation with the Log Correlation Engine (LCE). Using Tenable.sc CV, an organization will obtain the most comprehensive and integrated view of its network vulnerabilities.
This dashboard contains the following components:
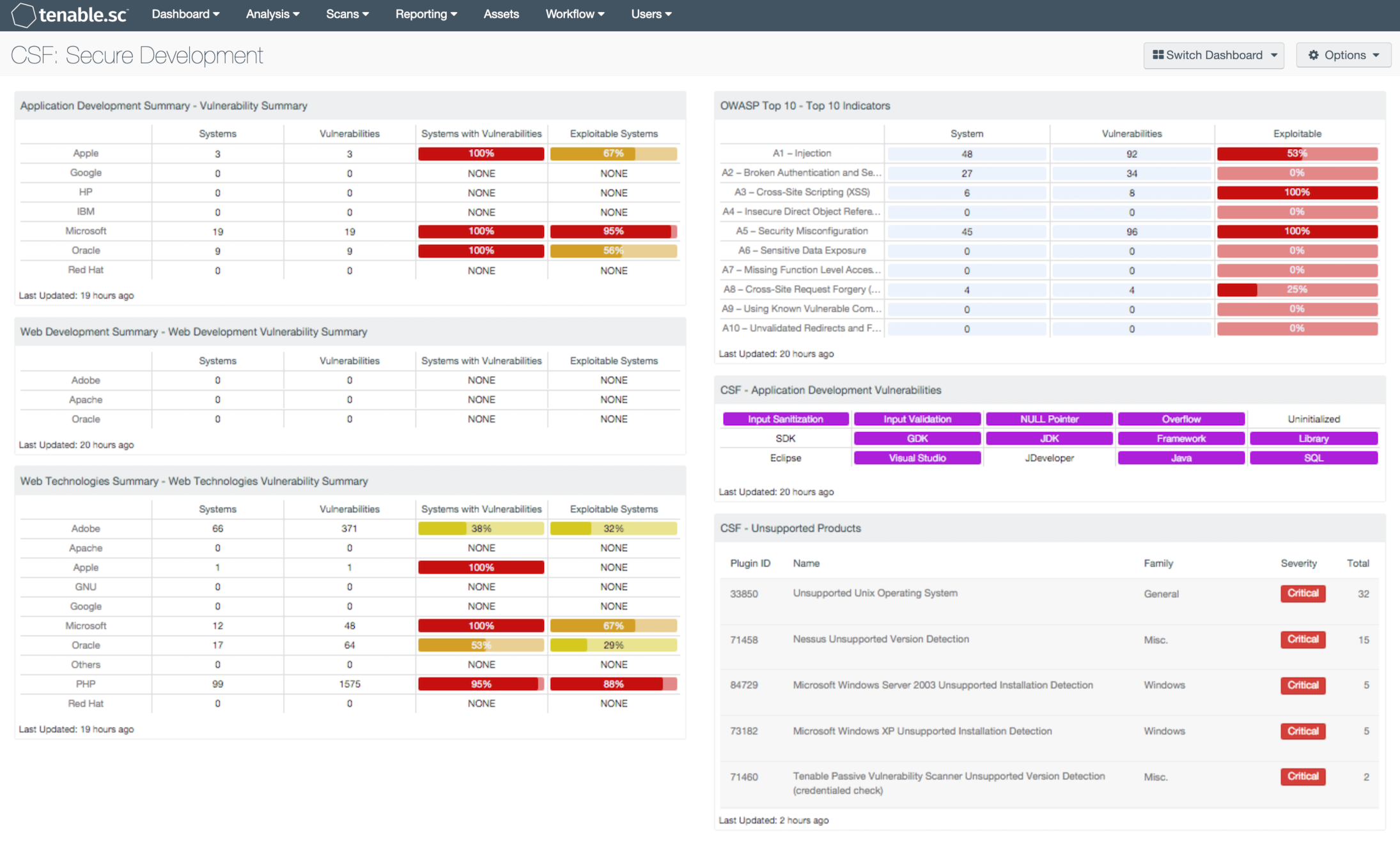
- Application Development Summary - Vulnerability Summary: This component displays various application development technologies by row, and enumerates any found vulnerabilities across the columns. Presented is the number of systems on which the technology has been located, the number of identified vulnerabilities, the ratio of vulnerable systems, and the count of how many are exploitable.
- Web Development Summary - Web Development Vulnerability Summary: This component displays various web development technologies by row, and enumerates any found vulnerabilities across the columns. Presented is the number of systems on which the technology has been located, the number of identified vulnerabilities, the ratio of vulnerable systems, and the count of how many are exploitable.
- Web Technologies Summary - Web Technologies Vulnerability Summary: This component displays various web technology technologies by row, and enumerates any found vulnerabilities across the columns. Presented is the number of systems on which the technology has been located, the number of identified vulnerabilities, the ratio of vulnerable systems, and the count of how many are exploitable.
- OWASP Top 10 - Top 10 Indicators: This component collects the vulnerabilities from the CGI Abuses, CGI Abuses : XSS, and Web Servers plugin families for both active and passive vulnerabilities. The CGI Abuses family Checks for web-based CGI programs with publicly documented vulnerabilities. These checks include SQL injection, Local File Inclusion (LFI), Remote File Inclusion (RFI), Directory Traversal, and more. For web-based CGI programs with publicly documented cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities, the CGI Abuses : XSS plugin family is used. For web server vulnerabilities, the Web Server plugin family can detect vulnerabilities in web servers such as Apache HTTP Server, IBM Lotus Domino, Microsoft IIS, and many more.
- CSF - Application Development Vulnerabilities: This component displays indicators for actively and passively detected vulnerabilities related to application development. Each indicator is highlighted purple if vulnerabilities with the given keyword(s) in their name are detected. The first row highlights common application development errors. The second row highlights vulnerabilities in development kits, frameworks, and libraries. The third row highlights vulnerabilities in several common IDEs and technologies. Note that because compliance failures are tracked as vulnerabilities, they will be included. An organization can develop its own Nessus or NNM plugins to discover vulnerabilities associated with its own internal software development; these detections will automatically appear here if the plugin names contain the appropriate keywords. New indicators can also be added as desired. Clicking on a highlighted indicator will bring up the vulnerability analysis screen to display details for the vulnerabilities and allow further investigation. In the analysis screen, setting the tool to IP Summary will display the systems on which the vulnerabilities are present. Setting the tool to Vulnerability Details will display the full details for each vulnerability, including a description, the solution to fix the vulnerability, and in some cases, links to more information.
- CSF - Unsupported Products: This table displays all unsupported products by name, sorted by severity. Displayed is the plugin ID, product name, plugin family, severity, and the total found. This component identifies unsupported products by filtering on the text "unsupported" in the vulnerability plugin name. Products and applications that are no longer supported can be serious security risks, as any vulnerabilities will no longer be patched by the vendor.